Insurance Service Provider
MS Dynamics CRM and the Power Platform provide significant advantages for the insurance industry, enabling companies to enhance customer relationships, streamline operations, and achieve better business outcomes. Here's how they help insurance businesses:
Lead Management and Automation
Scenario: A potential client submits a quote request form on the insurance company's website.
Solution:
1. Lead Capture: Dynamics CRM automatically captures lead information using Power Automate upon form submission.
2. Automated Follow-up: Power Automate triggers an email to the prospect, expressing gratitude and sharing more about the company's insurance offerings.
3. Lead Scoring: Dynamics CRM assigns a lead score based on interactions and engagement with the follow-up email.
4. Assignment: If the lead score meets the threshold, Power Automate routes the lead to the appropriate sales agent based on specialization or territory.
5. Lead Nurturing: If the lead isn't immediately ready for sales, Dynamics CRM initiates a nurture campaign through Power Automate, sending periodic valuable emails to maintain prospect interest.
Policy Renewal and Customer Retention
Scenario: A policyholder's auto insurance policy approaches its renewal date.
Solution:
1. Renewal Reminder: Dynamics CRM triggers an automated renewal reminder email via Power Automate, providing renewal options and a link to a personalized renewal portal.
2. Personalized Offer: Based on the policyholder's history and upsell potential, Dynamics CRM generates a tailored renewal offer using Power Automate.
3. Follow-up Calls: Agents receive schedules for follow-up calls to discuss renewal options, ensuring a personalized touch in the process.
4. Upselling/Cross-selling: Dynamics CRM suggests cross-selling opportunities to agents based on policyholder profiles, boosting revenue and customer satisfaction.
5. Document Management: Power Apps from the Power Platform creates a secure document upload portal for policyholders to submit necessary renewal documents.
Claims Processing and Customer Support
Scenario: A policyholder submits a claim following an accident.
Solution:
1. Claim Submission: Using a Power Apps portal, policyholders submit claim details, photos, and documents.
2. Claim Tracking: Dynamics CRM records claim details automatically and sends a confirmation email using Power Automate.
3. Automated Updates: Power Automate maintains policyholders informed about claim status, required documents, and expected timelines.
4. Agent Collaboration: Claims adjusters collaborate on claims using Dynamics CRM, accessing relevant customer information.
5. Communication History: Agents review the customer's communication history in Dynamics CRM, providing personalized support.
6. Resolution and Feedback: After claim resolution, Power Platform can send a survey to gather feedback, aiding process improvement.
Analytics and Reporting
Scenario: The insurance company seeks insights into sales performance and customer trends.
Solution:
1. Data Integration: Dynamics CRM integrates data sources to collect sales, customer, and claims information.
2. Custom Dashboards: Power BI generates customizable dashboards displaying key metrics such as policy sales, renewals, claims processing time, and satisfaction.
3. Sales Forecasting: Power Platform's predictive analytics assists in sales forecasting, enabling resource planning and goal setting.
4. Segmentation and Trends: Power BI segments customers and identifies trends, enabling targeted marketing campaigns.
5. Executive Insights: Real-time insights accessible through Power BI empower management to make data-driven decisions.
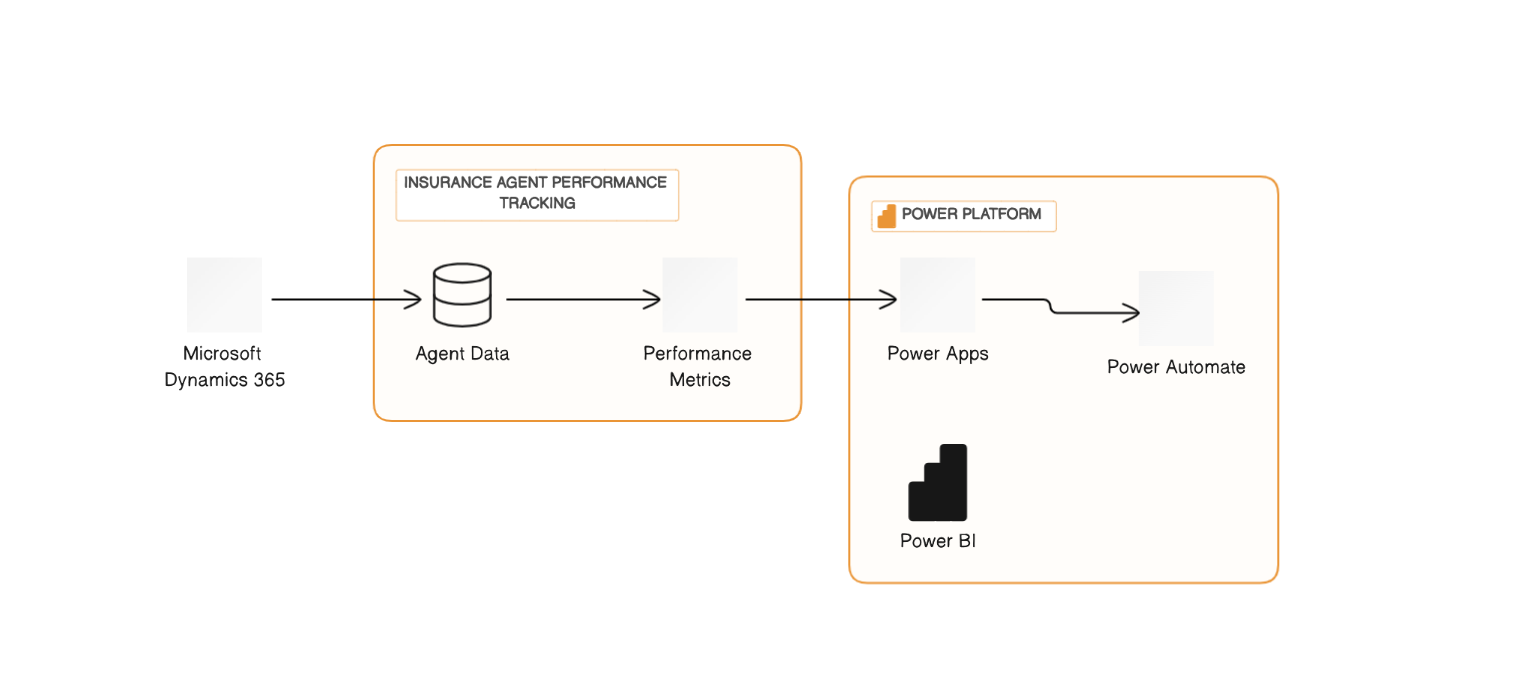
Agent Performance Tracking
Scenario: Insurance businesses, operating through agents, struggle to track and evaluate agent performance.
Solution:
1. Data Integration and Centralization: Dynamics CRM consolidates data from diverse sources, providing a unified view of agent activities and customer interactions.
2. Performance Metrics Definition: Define key performance metrics in Dynamics CRM, such as lead conversion rates and customer satisfaction scores.
3. Custom Dashboards and Reports: Power BI creates visual dashboards and reports in Dynamics CRM, offering insights into agent performance.
4. Automated Performance Alerts: Power Automate sends alerts via Dynamics CRM to agents and managers on meeting performance thresholds.
5. Performance Reviews and Coaching: Dynamics CRM aids in performance reviews, while Power Apps develop coaching tools for agents.
6. Incentive Programs: Dynamics CRM and Power Apps manage incentive programs based on agent performance metrics.
By embracing Microsoft Dynamics CRM and the Power Platform, insurance businesses optimize their operations, elevate customer experiences, and drive growth through automation, personalization, and data-based decisions.
###Business scenarios for a Microsoft Dynamics CRM insurance service business that offers a SuperCheck service on their website:
Scenario 1: SuperCheck Request and Lead Generation
* Lead Generation: A potential customer visits the insurance company's website and notices the "SuperCheck" service advertised.
* SuperCheck Inquiry: The customer clicks on the "SuperCheck" link to learn more and expresses interest in getting a SuperCheck for their insurance coverage.
* Lead Capture: The website captures the customer's contact information and insurance details through a web form. This information is entered into Microsoft Dynamics CRM as a lead.
* Lead Assignment: The CRM system assigns the lead to the appropriate agent or representative based on location or availability.
* Agent Contact: The assigned agent contacts the lead to schedule a SuperCheck conversation. They set up a meeting, either in person or via phone, for a detailed discussion.
Scenario 2: SuperCheck Conversation and Policy Review
* SuperCheck Appointment: The agent conducts a SuperCheck conversation with the customer, reviewing their current insurance coverage and understanding their insurance needs.
* Policy Evaluation: The agent uses Dynamics CRM to access the customer's insurance policies, regardless of the insurance company providing them. They analyze the policies to identify potential gaps or areas for improvement.
* Discount Assessment: During the conversation, the agent evaluates the customer's eligibility for discounts based on various criteria, such as bundled policies, safe driving history, or home security features.
* Policy Adjustments: If necessary, the agent recommends adjustments to the customer's existing policies or offers new policy options to address identified gaps.
Scenario 3: Annual SuperCheck Reminder
* Annual SuperCheck Reminder: The CRM system is configured to send annual SuperCheck reminders to existing customers who have previously undergone a SuperCheck or expressed interest.
* Customer Engagement: Customers receive email or SMS reminders encouraging them to schedule their annual SuperCheck with their agent.
* Appointment Scheduling: Customers can click on the reminder link to schedule their SuperCheck appointment directly through the CRM-integrated scheduling system.
* SuperCheck Follow-Up: After the SuperCheck conversation, the agent updates the customer's information in CRM, records any policy adjustments made, and schedules the next annual SuperCheck.
Scenario 4: SuperCheck Quiz and Self-Assessment
* SuperCheck Quiz: The insurance company's website features a SuperCheck quiz designed to help visitors assess if they might need a SuperCheck.
* Quiz Completion: Visitors take the short quiz, answering questions about life changes, assets, and insurance needs.
* Quiz Evaluation: Based on quiz responses, the website provides personalized recommendations, suggesting whether the visitor should consider a SuperCheck.
* Lead Generation: If the quiz indicates that a SuperCheck may be beneficial, the visitor is encouraged to submit their contact information to request a SuperCheck appointment, generating a new lead in CRM.
These scenarios demonstrate how Microsoft Dynamics CRM can support an insurance service business in managing SuperCheck requests, conducting policy reviews, and proactively engaging with customers to ensure their insurance coverage meets their evolving needs. The system helps capture leads, schedule appointments, and track SuperCheck outcomes for improved customer service and policy optimization.
###Business scenarios for a Microsoft Dynamics CRM insurance service business that utilizes Account Client Units (ACUs) to manage client relationships effectively:
Scenario 1: New Client Onboarding
* Client Acquisition: A new client purchases insurance policies from the insurance company.
* ACU Assignment: The new client is assigned to a specific ACU responsible for managing their account.
* Welcome Communication: The ACU sends a personalized welcome email or letter to the new client, introducing themselves and providing contact information for any questions or assistance.
* Policy Review: The ACU conducts a comprehensive review of the client's insurance policies to ensure they align with the client's needs and objectives.
* Policy Adjustments: If necessary, the ACU recommends policy adjustments or additional coverage options based on the client's unique situation.
Scenario 2: Policy Renewal and Cross-Selling
* Policy Renewal Notice: The CRM system generates policy renewal notices for clients whose policies are about to expire.
* ACU Outreach: The assigned ACU contacts clients to discuss policy renewals and explore opportunities for cross-selling additional coverage.
* Cross-Selling Recommendations: Based on the client's profile and needs, the ACU recommends relevant insurance products, such as adding life insurance to an existing auto policy.
* Renewal Confirmation: Clients confirm their policy renewals, and the ACU updates their policies accordingly.
Scenario 3: Claims Processing and Support
* Claim Submission: A client experiences an insurable event, such as a car accident, and needs to file a claim.
* ACU Assistance: The client contacts their assigned ACU for guidance on the claims process.
* Claim Documentation: The ACU assists the client in gathering the necessary documents and information to initiate the claim.
* Claims Tracking: The ACU tracks the progress of the claim within the CRM system, providing regular updates to the client.
* Claim Resolution: Once the claim is resolved, the ACU ensures that the client receives the appropriate compensation or repairs.
Scenario 4: Client Communications and Annual Reviews
* Annual Review Scheduling: The ACU proactively schedules annual insurance policy reviews with each client.
* Client Engagement: Clients receive reminders and invitations to participate in annual reviews, either in person or via phone.
* Policy Assessment: During the annual review, the ACU assesses any changes in the client's circumstances and insurance needs.
* Coverage Adjustments: Based on the review, the ACU may recommend adjustments to the client's policies to ensure they remain adequately covered.
Scenario 5: Lead Management and New Business Opportunities
* Lead Generation: The CRM system captures leads from various sources, such as website inquiries, referrals, or marketing campaigns.
* Lead Qualification: ACUs qualify leads by evaluating their insurance needs and readiness to purchase.
* Lead Nurturing: ACUs nurture leads through personalized communication and follow-up, educating them about available insurance options.
* Lead Conversion: Once a lead is ready to become a client, the ACU facilitates the conversion process, including policy selection and onboarding.
These scenarios illustrate how Microsoft Dynamics CRM, with the incorporation of ACUs, can enhance client relationship management, streamline insurance processes, and support client acquisition and retention in the insurance service business. ACUs play a central role in providing personalized service, policy optimization, and client support throughout the customer lifecycle.
###Business Scenarios for a Microsoft Dynamics CRM insurance service business sales, policy approval, and claim settlements
Scenario 1: Lead Conversion and New Client Onboarding
Lead Generation: An insurance agency receives leads from various sources, such as website inquiries, referrals, or marketing campaigns. These leads are entered into Dynamics CRM as potential clients (leads).
Lead Qualification: The sales team qualifies leads by evaluating their insurance needs and interest. Once qualified, the lead status is updated to "Qualified."
Lead Conversion: A qualified lead expresses interest in purchasing a policy. The lead is converted into a contact and an account in Dynamics CRM. The contact represents the individual client, and the account represents the client's organization if applicable.
Policy Creation: A custom policy entity in Dynamics CRM is used to create and manage policies for clients. A new policy is created for the converted contact, specifying coverage details, premium, and effective dates.
ACU Assignment: The newly converted client is assigned to an Account Client Unit (ACU) responsible for managing their account. The ACU ensures a smooth onboarding process, answers client questions, and assists with policy details.
Policy Documentation: Policy documents are generated within Dynamics CRM and sent to the client for review and e-signature. The system tracks document status and notifies the ACU when the client signs the policy.
Scenario 2: Policy Quoting and Approval
Quote Request: An existing client contacts their assigned ACU requesting a quote for additional coverage, such as adding a new vehicle to their auto policy.
Quote Creation: The ACU creates a new quote within Dynamics CRM, specifying the requested coverage and premium details. The quote is associated with the client's policy.
Quote Presentation: The quote is sent to the client for review, either through email or a secure client portal integrated with Dynamics CRM.
Client Approval: The client reviews the quote and provides approval. This approval is recorded within Dynamics CRM, and the quote status is updated accordingly.
Policy Update: Once the quote is approved, the ACU updates the client's policy within Dynamics CRM to reflect the new coverage. The system automatically calculates the revised premium.
Scenario 3: Claims Processing
Claim Submission: A client contacts their assigned ACU to report an insurance claim, such as a car accident or property damage.
Claim Creation: The ACU logs the claim details in Dynamics CRM using a custom claims entity, including incident information, photos, and relevant documents.
Claim Assignment: The claim is assigned to a claims adjuster or processor within the ACU responsible for managing claims.
Claim Investigation: The claims adjuster conducts an investigation, contacts witnesses if necessary, and assesses the claim's validity.
Claim Resolution: After investigation, the claim is resolved. If approved, the system generates a payment request, and the client is reimbursed according to the policy terms.
These scenarios illustrate how Microsoft Dynamics CRM can streamline processes for an insurance service business, from lead generation and client onboarding to policy management, quoting, and claims processing. Custom entities are used to capture specific insurance-related information, and ACUs play a crucial role in managing client relationships and interactions.
High-level architecture: https://app.eraser.io/workspace/yCu9CMZfbLzjORk5IQSS?origin=share